Today, with the advancement of technology, we are witnessing the use of new materials in the construction industry. Among the many types of materials that can be used in the roof of structures, the sandwich panel roof has numerous advantages. This type of panel is used as a wall in the construction of the roof of sheds, huts, prefabricated houses, etc.
As explained in the article “What is a sandwich panel?“, The sandwich panel consists of a middle layer of insulating foam, bounded on both sides by two layers of sheet metal. The material and thickness of each of these three layers can be changed depending on the intended application. One of the main differences between roof sandwich panels and wall sandwich panels is the sheet form used in the upper layer. The trapezoidal structure of the sheet directs water from snow and rainfall to the drain. In the following, we will introduce the types of roof sandwich panels, their advantages and applications.
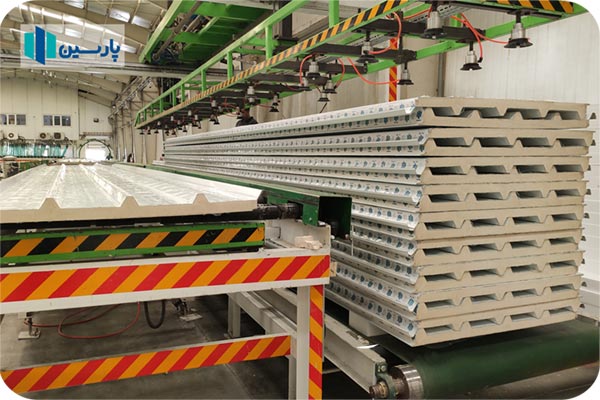

Types of ceiling sandwich panels
Ceiling sandwich panels are divided into two types:
- Double-sided ceiling sandwich panel
- Single-sided ceiling sandwich panel
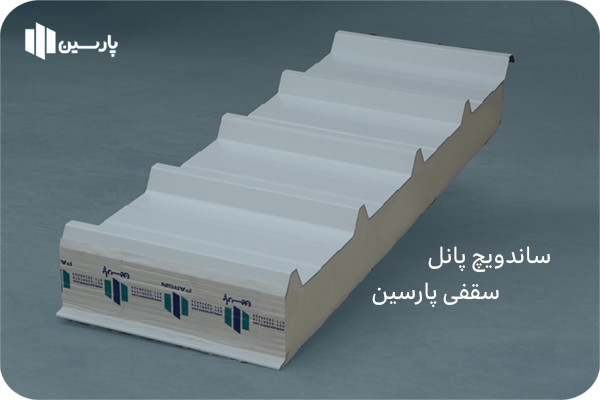
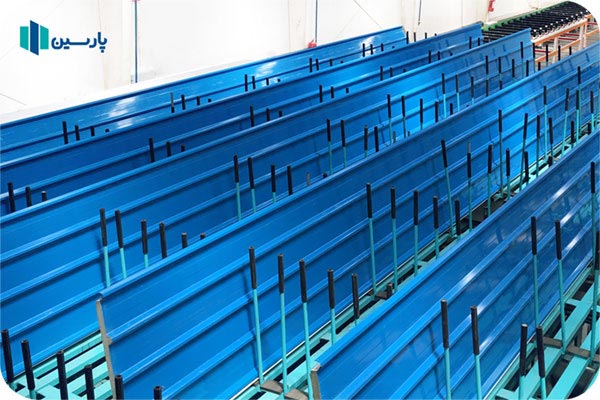
Sandwich panel manufacturing companies produce roof panels with different pitch numbers. Thus, the number of pitches of a roof sandwich panel can range from 3 to 5 pitches. The width of the top sheet used in the production of sandwich panels for roof panels is 3 pitches less than the width of the sheet required to produce a 5-pitch roof sandwich panel.
Also, the fewer the number of steps in a roof sandwich panel, the lower its resistance. Accordingly, Parsin Company has produced 5-step roof sandwich panels, which provide the best resistance and efficiency for the consumer.
Material of roof sandwich panel layers
The upper or outer layer has a trapezoidal shape and is generally made of steel alloys such as galvanized, aluzinc, aluminum, etc. This layer prevents moisture penetration and directs rainwater through the channels between the trapezoidal cross-sections towards the river. The bottom or inner layer, depending on the consumer’s order, is either made of steel alloys like the top layer or sometimes, to reduce price and weight, it is made of kraft paper, reinforced aluminum, etc. This coating is the visible layer under the roof, which can be changed depending on the need.
The core of roof sandwich panels is usually made of materials such as polyurethane, etc. to provide insulation against the penetration of external temperature caused by solar radiation on the roof surface in hot seasons and also to provide insulation against the escape of heat generated by the interior space in cold seasons.
Benefits of using ceiling sandwich panels
Some of the benefits of using ceiling sandwich panels are listed below. Considering the following, the price of ceiling sandwich panels will also be affordable compared to other building materials.
- Low weight
- Easy installation
- Very low heat transfer coefficient
- High execution speed
- Easy transportation
- Possibility of dismantling and opening the sandwich panels at any time
- High durability compared to other building materials
- Good moisture and sound insulation
- High color variety in consumable sheets
How to install ceiling sandwich panels
The method of connecting the roof sandwich panel to the structure is by means of bolts and washers. This type of connection, in addition to meeting the required standards for structural connections, also allows for easy disassembly of temporary roofs. The tongue and groove intended for the sandwich panel results in overlapping of the empty and full steps, which is important in the process of installing and sealing roofs and also facilitates the installation operation.
Applications of ceiling sandwich panels
In the not-so-distant past, using a combination of galvanized sheets, mesh, and glass wool as roof coverings was considered one of the most important industrial materials. However, with the gradual production of various types of ceiling sandwich panels, such as single-sided sheet and single-sided reinforced aluminum foil sandwich panels, and given its competitive cost compared to traditional materials, this product is considered a suitable alternative to traditional materials.
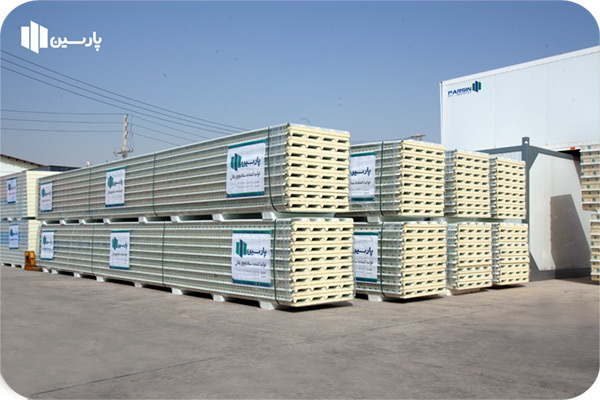

To protect the roof of various structures against natural factors such as storms, rain, snow and to prevent heat transfer, moisture penetration, sunlight, etc., a highly resistant coating is required. Using polyurethane sandwich panels with galvanized sheets, aluminum, etc. In the roof covering of structures, in addition to providing the desired resistance, it reduces heat transfer and, on the other hand, has low weight and a suitable appearance.
Nowadays, due to the development of the construction industry, the application of modern construction materials has no specific limits and in fact the consumer determines the type of application of the materials in his project. However, the history of the application of ceiling sandwich panels mainly shows itself in the following cases:
- Prefabricated houses and cabins
- Small and large warehouses
- Industrial sheds
- Sports halls
- Entertainment halls
- swimming pools
- Military shelters
- Gazebos
- Parking lots
- and…
Types of ceiling sandwich panels by sheet type
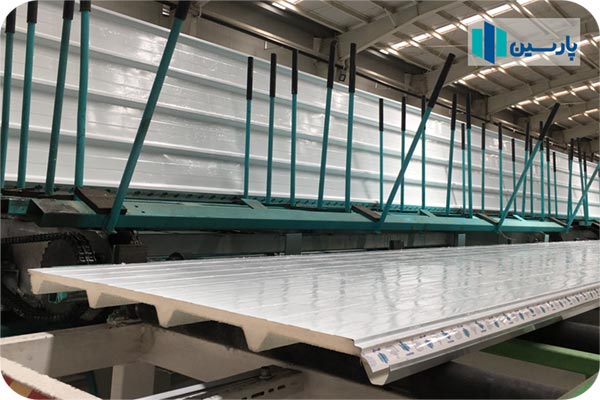
The sheet covering and thickness of the roof sandwich panels produced by Parsin Gostar Junob Company are highly diverse and tailored to the needs of the consumer. As mentioned earlier, the upper or outer layer of the roof sandwich panel is insulated against external factors such as snow and rain, sunlight, etc. It should mainly be made of steel alloys, which include a wide range of alloys such as galvanized, aluzinc, aluminum, etc., with thicknesses ranging from 0.4 mm to 0.7 mm.
The outer surface of the sheets is coated with 25 micron thick baked polyester, and 7 microns of baked primer paint is applied to the inside to create better adhesion between the foam and the sheet.

The bottom or inner layer of ceiling sandwich panels is important because it is visible from inside the space; but this importance is determined by the end consumer. This means that in projects where this layer is not the final layer and another layer is eventually built as a false ceiling, lighter coatings such as reinforced aluminum foil, kraft paper, nylon, etc. can be used in this layer to both reduce the total dead weight of the ceiling and minimize the total cost.
Otherwise, this layer, like the upper or outer layer, is produced from steel alloys with the same diverse range of galvanized, aluzinc, aluminum, etc., with different thicknesses from 0.4 mm to 0.7 mm.
Types of ceiling sandwich panels in terms of foam thickness
The thickness of the insulation core of Parsin ceiling sandwich panels can be changed from 2 cm to 10 cm. Depending on the type of consumer’s needs, ceiling sandwich panels with smaller thicknesses are used in projects that require a smaller thickness of insulation, such as parking lots, non-food warehouses, etc.

Parsin Gostar Junob Company has taken an effective step towards reducing energy consumption and increasing the lifespan of building materials by producing 2 cm thick ceiling sandwich panels, one side of which is covered with reinforced aluminum foil. This is achieved by replacing polyurethane foam with traditional and old materials such as glass wool, rock wool, etc.
Also, in projects where the difference between internal and external temperatures is high, such as industrial cold stores, sheds in tropical or cold regions, etc., higher thickness roof sandwich panels are used. Due to the high thickness of the foam used in these types of panels, the heat transfer rate is very low, and as a result, energy consumption costs are also reduced.





















